- 6 min read
- Oct 29, 2024
- 0
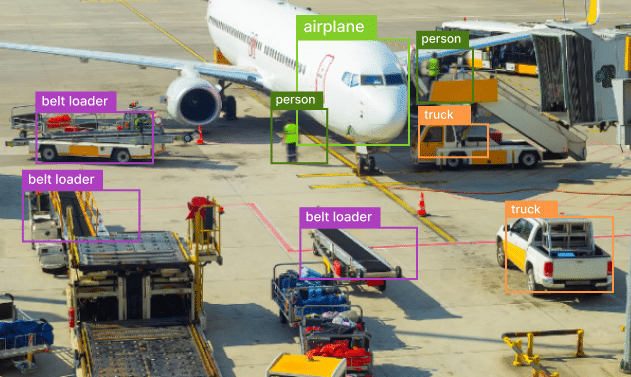
The aviation industry is considered a relevant sector that effectively relies on precision, accuracy and safety. Technological advancements are becoming increasingly popular among various sectors contributing to overall operational efficiency and improving safety measures. Computer vision is an application of AI that allows machines to interpret and comprehend digital images. Applications of computer vision technology are quite varied comprising finding planes and recognizing management, airport security enabling drones to fly and guiding other air jets. In this blog post, we are going to explore the role of computer vision in the aviation industry. As airlines are increasing, airports are adopting the technology to streamline operations and improve safety measures. In recent years, the utilization of computer vision technology has streamlined operations and improved safety measures in the aviation industry.
What are the challenges faced by the aviation industry?
The aviation industry is filled with a wide range of challenges and some of the relevant challenges involve safety, cost control, security, and regulations. Let’s take a look at the different challenges confronted by the aviation industry.
Safety: Safety is one of the most relevant challenges confronted by the aviation industry. It has made great strides in advancing safety through training, technology and regulation manually.
Security: Having the increased threat of terrorism and various other security concerns, the aviation industry should continuously adapt and improve its security measures for protecting passengers and aircraft.
Cost control: Airlines are continuously working to cut costs while maintaining quality levels of service. Controlling costs can be difficult in aviation industries as cost distributions are huge. Airport maintenance, labor costs, and airport fees have a valuable impact on the airline’s profitability.
Regulations: The Aerospace industry is mainly subjected to a complex series of local, international and national regulations. It can be time-consuming for airlines to manually take care of the computer vision in the aviation sector.
Major use cases of computer vision in the aviation industry
Potential security & surveillance
The aviation industry harnesses Computer vision AI and IoT technologies for improving security and surveillance measures detecting security breaches, theft and vandalism. It comprises features such as object detection, facial recognition, and passenger behavior monitoring through IP cameras. The AI video surveillance system can identify potential threats, allow effective operations and improve passenger flow.
Predictive maintenance

As per the latest report, it can be estimated that the global market size is expected to grow from USD 1.5 billion in the year 2020 to USD 3.8 billion by 2025 at a CAGR of 20%. This ample growth is determined by the increasing demand for automation and safety measures in the aviation industry. From real-time monitoring and analysis of aircraft elements to improving safety and diminishing maintenance costs. With the implementation of predictive analysis, potential maintenance glitches can be detected on time and repairs can be conducted preventing any major faults that could potentially increase expenses. With Computer Vision for Aviation Safety, it is possible to inspect aircraft elements, predict maintenance, enable timely repairs and prevent breakdowns in the aviation sector.
Real-time tracking of passengers
Computer vision technology can seamlessly track passenger movements in the aviation sector, detect and analyze passenger behavior, recognize potential security risks, monitor crowd density and optimize passenger flow. It is valuable in security checkpoints, boarding gates, and baggage handling areas for embellishing safety protocols.
Object detection & recognition
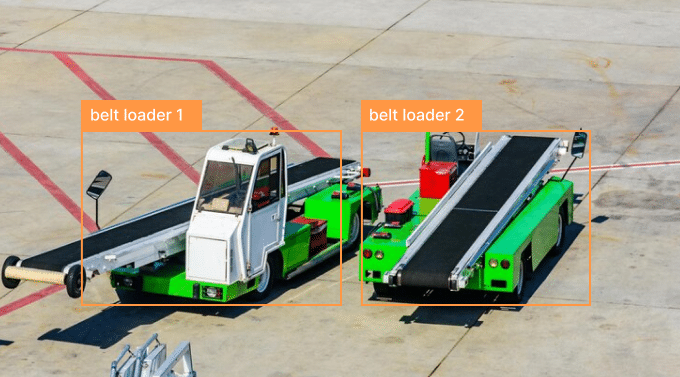
Using computer vision, object detection and recognition can improve security and safety measures within the aviation sector. Empowered with object detection, the technology can track and detect objects in real-time enabling early detection of potential hazards and faster response times. It is majorly used for baggage screening, aircraft maintenance and runway surveillance, thereby effectively streamlining airport operations.
Intelligent baggage handling
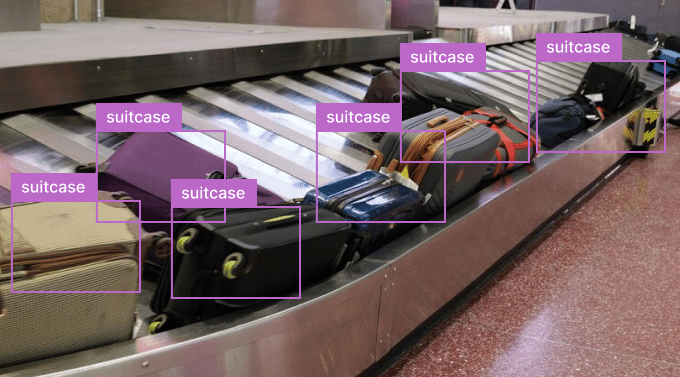
Deep learning systems can automatically read labels with machine vision to detect trolleys and their respective locations. It assists in improving the efficiency of the baggage handling process and diminishes the chances of lost luggage. Computer vision systems harness cameras for scanning the tags on luggage and matching them with valuable data in the airline database. Visual deep-learning applications assist in identifying and localizing ground vehicles at airports. It increases the efficacy of managing and distributing baggage carts. AI in Object detection can be used to prevent major terror incidents by early identification of unknown objects at airports.
Face recognition
Facial recognition powered by computer vision AI can identify passengers at airports. AI software helps in comparing the passenger’s face to a database of images that have been pre-loaded into the system. It can perform face detection and recognition with IP cameras. The technology is empowered to streamline the boarding process and ensure that all passengers have boarded the plane. For investigation purposes, it is used to identify suspected criminals.
Cargo inspection & AI computer vision
With the utilization of advanced computer vision algorithms, airport authorities can inspect the cargo for any kind of potential threats comprising weapons, explosives, and narcotics. AI-powered cargo inspection assists in speeding up the process of cargo security processes. Harnessing deep learning models, the technology applies pattern recognition to image data from cameras. Neural networks are trained to detect annotated images of explosive materials.
Airport safety & security
Computer vision can be seamlessly integrated into airport security applications. Within airport infrastructure cameras placed in important locations enable airport authorities to track people and object’s movements. Data updated in real-time assists in finding possible security threats and improving overall airport security. AI surveillance can be used to identify people trying to climb over fences, create large-scale heatmaps, observe perimeters for intrusions, and analyze movement patterns.
Some valuable uses of computer vision involve real-time crowd analysis & crowd monitoring, tracking the movement of people & objects, diminishing the number of false positives in security checks, and fire & smoke detection.
Computer vision AI in missile guidance
Artificial intelligence has come a long way with its immense potential to assist different fields of aerial weapon systems in military and defense applications. Vision AI plays a major role in guiding missiles and automates the process of operation seamlessly. By identifying the location and motion of objects, computer vision helps ensure that missiles target with accuracy. Image processing technology combined with intelligent AI sensors can detect any target while conventional detection is restricted to fire, heat and other signals.
Key Takeaways
The aviation industry is making valuable use of computer vision for different applications for a wide range of purposes. Latest advances in emerging technologies enable the development of strategic robust machine learning solutions while significantly improving the cost of computer vision. The implementation of computer vision technology comes up with major challenges like extensive data processing capabilities and seamless integration with existing systems.
Do you want to learn more about AI video analytics software and its applications in the aviation industry? Are you on the lookout for an advanced intelligence solution? Get in touch with our professionals and delve deeper into AI.

